Shipbuilding industry worldwide - statistics & facts
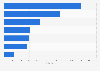
The leading shipbuilding companies worldwide include South Korean Hyundai HI, Daewoo Shipbuilding, and Samsung HI, Chinese China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation and China State Shipbuilding Corp., as well as Japanese Mitsubishi HI. European and North American shipyards, such as Philly Shipyard and General Dynamics NASSCO, are more prone to operating in the field of cruise, yacht, and military ships.
Impact of COVID-19
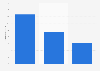
After East Asian countries became the dominant players in the cargo shipbuilding industry in the late 20th century, knowing they could not compete with the East Asian competition, European shipyards started specializing in the production of passenger vessels. Up until the COVID-19 pandemic broke out in 2019, this strategy was paying off. While Asian shipyards were suffering from insufficient demand and overcapacity of shipyards, European ship manufacturers were thriving. The COVID-19 pandemic, however, disrupted this status quo. With passenger travel coming to a standstill, especially in the cruise industry, the demand for new passenger vessels at European shipyards plummeted. East Asian ship producers, on the other hand, were having trouble meeting the rising demand for cargo ships in the first months of 2021.Short history of shipbuilding
Humans started building ships many thousands of years ago, as the construction of ships or floating vessels enabled them to expand their populations beyond their own continental dwellings. As societies developed and progressed, shipbuilding further allowed civilizations to take part in commercial trade with lands far from their own. Furthermore, it equipped those civilizations with large naval fleets to participate in sea-faring conquests to explore and conquer new lands. Traditional ships depended on human power and wind to propel vessels across waters. With the onset of the Industrial Revolution, ships were then able to use new materials, designs, and propulsions systems, including the steam engine, to improve the quality of commercial and military vessels.Nowadays, ships are predominantly equipped with internal combustion engines powered by fuel oil. Although cheap and widely available, fuel oil is a major air pollutant. Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from shipping accounted for 11 percent of total global emissions in 2020.