Ocean shipping worldwide - statistics & facts
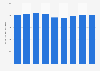
Despite these developments, the COVID-19 pandemic caused severe disruptions to the ocean shipping industry that are only slowly disappearing. As a result, the volume of cargo transported by ships in 2021 was still slightly lower than in 2019, the year before the pandemic struck.
Impact of COVID-19 on the industry
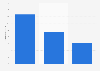
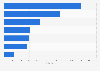
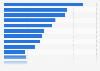
The COVID-19 pandemic hit the global shipping industry especially hard. Ports had to deal with closures, resulting in congestions, labor shortages, and blank sailings. At the same time, container carriers struggled with capacity utilization and ship delays, bringing schedule reliability of major container ship operators below 40 percent for most of 2021. On top of that, freight rates skyrocketed, putting pressure on industries that rely on exports and imports of commodities and goods. In turn, consumers all around the globe were forced to bear the rising costs of transport in increasing prices, with the inhabitants of small island developing states being affected the most.Finally, in the second half of 2022, the situation began to improve. Schedule reliability has increased, and freight rates have normalized, dropping to nearly pre-pandemic levels. Subsequently, the profit margins of container carriers have decreased significantly, from their peak of 57.4 percent in the first quarter of 2021 to 8.9 percent in the second quarter of 2023. Still, the container shipping industry reported record-high profits of some 208 billion U.S. dollars in 2022, almost double its profit in 2021.