
Bergur Thormundsson
Research expert covering technology in the Nordics, AI and smart cities

Detailed statistics
AI market size worldwide from 2020-2031

Detailed statistics
AI market size worldwide from 2020-2031

Detailed statistics
Market size of AI in the United States 2020-2031

Detailed statistics
Market size of AI in the United States 2020-2031

Detailed statistics
Market size of AI in Europe 2020-2031

Detailed statistics
Market size of AI in Europe 2020-2031

Market size of large language models in China 2022-2027
Size of large language model market in China from 2022 to 2023 with estimates until 2027 (in billion yuan)

Market size of large language models in China 2022-2027
Size of large language model market in China from 2022 to 2023 with estimates until 2027 (in billion yuan)

LLM market size in Japan FY 2024-2028
Value of the large language model (LLM) market in Japan in fiscal year 2024 with a forecast for 2028 (in billion Japanese yen)

LLM market size in Japan FY 2024-2028
Value of the large language model (LLM) market in Japan in fiscal year 2024 with a forecast for 2028 (in billion Japanese yen)

Market size of large AI models in China 2020-2026
Size of large artificial intelligence model market in China from 2020 to 2023 with estimates until 2026 (in billion yuan)

Market size of large AI models in China 2020-2026
Size of large artificial intelligence model market in China from 2020 to 2023 with estimates until 2026 (in billion yuan)
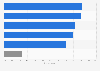
Most wanted financial applications of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models in the financial segment in China as of September 2024

Most wanted financial applications of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models in the financial segment in China as of September 2024

Firms planned LLM model usage in commercial deployments worldwide 2024
Organizations planned large language model (LLM) utilization for commercial deployment worldwide in 2024

Firms planned LLM model usage in commercial deployments worldwide 2024
Organizations planned large language model (LLM) utilization for commercial deployment worldwide in 2024
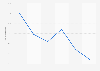
Growth of the large AI model market in China 2021-2026
Growth rate of the large artificial intelligence model market in China from 2021 to 2023 with estimates until 2026

Growth of the large AI model market in China 2021-2026
Growth rate of the large artificial intelligence model market in China from 2021 to 2023 with estimates until 2026

Global ranking of LLM tools in 2023
Ranking of large language model (LLM) tools worldwide in 2023

Global ranking of LLM tools in 2023
Ranking of large language model (LLM) tools worldwide in 2023

Ranking of LLM tools in solving math problems 2024
Ranking of large language model (LLM) tools in solving math problems worldwide in 2024

Ranking of LLM tools in solving math problems 2024
Ranking of large language model (LLM) tools in solving math problems worldwide in 2024

Leading large AI model segments according to respondents in China 2024
Leading large artificial intelligence segments that users pay attention to in China as of September 2024

Leading large AI model segments according to respondents in China 2024
Leading large artificial intelligence segments that users pay attention to in China as of September 2024
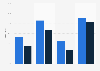
AI citations vs Google Search results overlap 2025
Overlap of AI citations vs top 10 ranking Google Search results in June 2025

AI citations vs Google Search results overlap 2025
Overlap of AI citations vs top 10 ranking Google Search results in June 2025

Most wanted e-commerce applications of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models in the e-commerce segment in China as of September 2024

Most wanted e-commerce applications of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models in the e-commerce segment in China as of September 2024

Benchmark scores Kanana LLM 2024, by type
Benchmark scores of Kanana large language models (LLMs) in 2025, by type

Benchmark scores Kanana LLM 2024, by type
Benchmark scores of Kanana large language models (LLMs) in 2025, by type

MAU of MiniMax's Xingye AI app users 2024
Monthly active users of MiniMax's GenAI chatbot Xingye AI app from May to September 2024 (in million users)

MAU of MiniMax's Xingye AI app users 2024
Monthly active users of MiniMax's GenAI chatbot Xingye AI app from May to September 2024 (in million users)

MAU of Moonshot AI's Kimi Chat app 2024
Monthly active users of Moonshot AI's GenAI chatbot Kimi Chat app from May to September 2024 (in million users)

MAU of Moonshot AI's Kimi Chat app 2024
Monthly active users of Moonshot AI's GenAI chatbot Kimi Chat app from May to September 2024 (in million users)

MAU of Zhipu AI's Zhipu Qingyan app 2024
Monthly active users of Zhipu AI's GenAI chatbot Zhipu Qingyan app from May to September 2024 (in million users)

MAU of Zhipu AI's Zhipu Qingyan app 2024
Monthly active users of Zhipu AI's GenAI chatbot Zhipu Qingyan app from May to September 2024 (in million users)
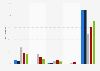
Ranking positions of LLM-cited search results 2025
Ranking positions of search results cited by large language models (LLMs) as of June 2025

Ranking positions of LLM-cited search results 2025
Ranking positions of search results cited by large language models (LLMs) as of June 2025
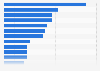
Top web domains cited by LLMs 2025
Top web domains cited by large language models (LLMs) in June 2025

Top web domains cited by LLMs 2025
Top web domains cited by large language models (LLMs) in June 2025

Most wanted cybersecurity applications of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models in the cybersecurity segment in China as of September 2024

Most wanted cybersecurity applications of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models in the cybersecurity segment in China as of September 2024
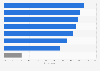
Most wanted healthcare applications of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models in the healthcare segment in China as of September 2024

Most wanted healthcare applications of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models in the healthcare segment in China as of September 2024
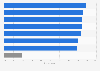
Most wanted educational applications of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models in the education segment in China as of September 2024

Most wanted educational applications of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models in the education segment in China as of September 2024

Frequency of using large AI models in China 2024
Frequency of using large artificial intelligence models in China as of September 2024

Frequency of using large AI models in China 2024
Frequency of using large artificial intelligence models in China as of September 2024
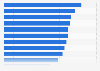
Most wanted application fields of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models among users in China as of September 2024

Most wanted application fields of large AI models in China 2024
Most anticipated areas of application of large artificial intelligence models among users in China as of September 2024

Main use of large AI models in China 2024
Main applications of large artificial intelligence models in China as of September 2024

Main use of large AI models in China 2024
Main applications of large artificial intelligence models in China as of September 2024
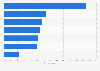
Most popular use of generative AI in China 2024
Main applications of generative AI in China as of June 2024

Most popular use of generative AI in China 2024
Main applications of generative AI in China as of June 2024

Number of large AI model applications in China 2024, by type
Breakdown of the number of large artificial intelligence model applications in China as of the 6th filing round in 2024, by type

Number of large AI model applications in China 2024, by type
Breakdown of the number of large artificial intelligence model applications in China as of the 6th filing round in 2024, by type

Generative AI market size in China 2023-2028
Size of the generative artificial intelligence market in China in 2023 and 2024, with a forecast until 2028 (in million U.S. dollars)

Generative AI market size in China 2023-2028
Size of the generative artificial intelligence market in China in 2023 and 2024, with a forecast until 2028 (in million U.S. dollars)

Breakdown of interest in generative AI segments in Taiwan Q4 2023
Share of public interest in generative AI in Taiwan in 4th quarter of 2023, by segment

Breakdown of interest in generative AI segments in Taiwan Q4 2023
Share of public interest in generative AI in Taiwan in 4th quarter of 2023, by segment

Use of AI chatbots in South Korea 2023, by generation
Use of artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots in South Korea as of July 2023, by generation

Use of AI chatbots in South Korea 2023, by generation
Use of artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots in South Korea as of July 2023, by generation
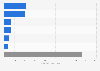
Number of large AI model applications in China 2024, by category
Breakdown of the number of large artificial intelligence model applications in China as of the 6th filing round in 2024, by category

Number of large AI model applications in China 2024, by category
Breakdown of the number of large artificial intelligence model applications in China as of the 6th filing round in 2024, by category
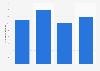
Number of large AI model applications in China 2024, by company size
Breakdown of the number of large artificial intelligence model applications in China as of the 6th filing round in August 2024, by company size

Number of large AI model applications in China 2024, by company size
Breakdown of the number of large artificial intelligence model applications in China as of the 6th filing round in August 2024, by company size

Number of web users of leading generative AI products in China 2024
Leading generative artificial intelligence products in China in September 2024, based on the number of web users (in millions)

Number of web users of leading generative AI products in China 2024
Leading generative artificial intelligence products in China in September 2024, based on the number of web users (in millions)

Number of large AI model applications per filing round in China 2023-2024
Number of large artificial intelligence model applications per filing rounds in China from June 2023 to August 2024

Number of large AI model applications per filing round in China 2023-2024
Number of large artificial intelligence model applications per filing rounds in China from June 2023 to August 2024

Number of large AI model applications in China 2024, by use case
Breakdown of the number of large artificial intelligence model applications in China as of the 6th filing round in 2024, by use case

Number of large AI model applications in China 2024, by use case
Breakdown of the number of large artificial intelligence model applications in China as of the 6th filing round in 2024, by use case

Mistral ML2 MMLU benchmark comparison in 2024
Benchmark comparison of Mistral's ML2 with major generative artificial intelligence (AI) model competitors in 2024

Mistral ML2 MMLU benchmark comparison in 2024
Benchmark comparison of Mistral's ML2 with major generative artificial intelligence (AI) model competitors in 2024

Uses of LLMs in healthcare organizations in the United States 2024
Cases for which healthcare organizations use large language models (LLMs) in the United States in 2024

Uses of LLMs in healthcare organizations in the United States 2024
Cases for which healthcare organizations use large language models (LLMs) in the United States in 2024

Perceived impact of LLMs in healthcare organizations in the U.S. 2024
Mean rating of large language models (LLMs) on use cases in healthcare organizations in the United States as of 2024

Perceived impact of LLMs in healthcare organizations in the U.S. 2024
Mean rating of large language models (LLMs) on use cases in healthcare organizations in the United States as of 2024

Most popular AI chatbots in China 2024
Leading artificial intelligence chatbots in China as of June 2024, based on usage rate

Most popular AI chatbots in China 2024
Leading artificial intelligence chatbots in China as of June 2024, based on usage rate

Total funding of LLM developers worldwide in 2023
Large language model artificial intelligence (AI) developer funding globally in 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)

Total funding of LLM developers worldwide in 2023
Large language model artificial intelligence (AI) developer funding globally in 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)

Ways AI chatbots are used in South Korea 2023
Distribution of uses cases for artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots in South Korea as of July 2023

Ways AI chatbots are used in South Korea 2023
Distribution of uses cases for artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots in South Korea as of July 2023

Ways AI chatbots are used in South Korea 2023, by generation
Distribution of uses cases for artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots in South Korea as of July 2023, by generation

Ways AI chatbots are used in South Korea 2023, by generation
Distribution of uses cases for artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots in South Korea as of July 2023, by generation

Performance of DeepSeek-R1 compared to similar models in English benchmarks 2025
English language performance comparison between DeepSeek R-1model and similar models in 2025, by benchmark

Performance of DeepSeek-R1 compared to similar models in English benchmarks 2025
English language performance comparison between DeepSeek R-1model and similar models in 2025, by benchmark
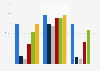
Performance of DeepSeek-R1 compared to similar models in mathematics benchmarks 2025
Mathematics performance comparison between DeepSeek R-1 model and similar models in 2025, by benchmark

Performance of DeepSeek-R1 compared to similar models in mathematics benchmarks 2025
Mathematics performance comparison between DeepSeek R-1 model and similar models in 2025, by benchmark

Performance of DeepSeek-R1 compared to similar models in Chinese benchmarks 2025
Chinese language performance of DeepSeek R-1model and similar models in 2025, by benchmark

Performance of DeepSeek-R1 compared to similar models in Chinese benchmarks 2025
Chinese language performance of DeepSeek R-1model and similar models in 2025, by benchmark

Daily active users of DeepSeek 2025
Daily active users of DeepSeek from January 11 to February 15, 2025 (in millions)

Daily active users of DeepSeek 2025
Daily active users of DeepSeek from January 11 to February 15, 2025 (in millions)

MAU of Baidu's Wenxiaoyan 2024, by type of access
Monthly active users of Baidu's GenAI chatbot Wenxiaoyan from January to August 2024, by type of access (in million users)

MAU of Baidu's Wenxiaoyan 2024, by type of access
Monthly active users of Baidu's GenAI chatbot Wenxiaoyan from January to August 2024, by type of access (in million users)

Awareness of AI chatbots in South Korea 2023, by generation
Awareness of artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots in South Korea as of July 2023, by generation

Awareness of AI chatbots in South Korea 2023, by generation
Awareness of artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots in South Korea as of July 2023, by generation

Market size of large health AI models in China 2023-2030
Market size of large AI models in the medical sector in China in 2023 with estimates until 2030 (in billion yuan)

Market size of large health AI models in China 2023-2030
Market size of large AI models in the medical sector in China in 2023 with estimates until 2030 (in billion yuan)
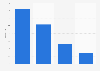
Training token requirement EXAONE 3.5 compared to similar models 2024
Training token requirement of EXAONE 3.5 compared to similar models in 2024

Training token requirement EXAONE 3.5 compared to similar models 2024
Training token requirement of EXAONE 3.5 compared to similar models in 2024

Performance of DeepSeek-R1 compared to OpenAI in leading benchmarks 2025
Performance comparison of DeepSeek R-1 and OpenAI-o1-1217 in 2025, by benchmark

Performance of DeepSeek-R1 compared to OpenAI in leading benchmarks 2025
Performance comparison of DeepSeek R-1 and OpenAI-o1-1217 in 2025, by benchmark
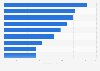
Korean language benchmarks HyperCLOVA X compared to open-source models 2024
Korean language benchmarks of HyperCLOVA X compared to open-source models in 2024

Korean language benchmarks HyperCLOVA X compared to open-source models 2024
Korean language benchmarks of HyperCLOVA X compared to open-source models in 2024


Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)