RPI in the UK 2000-2024
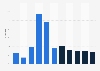
The Retail Price Index (RPI) is one of the main measures of inflation used to calculate the change in the price of goods and services within the British economy. In the third quarter of 2024 the index value was 388.7, indicating that the price for a fixed basket of goods had increased by more than 288 percent since 1987. The RPI inflation rate for September 2024 was 2.7 percent, down from 3.5 percent in the previous month. Between April 2022 and June 2023, the RPI inflation rate was consistently in double-figures, but appears to have peaked at 14.2 percent in October 2022, with inflation falling gradually since then.
Inflation stuck at high levels in 2023
Although there has been a fall in inflation since October 2022, inflation is still at quite high levels in the UK, and has not fallen as fast as the government would have hoped. According to forecasts from the Spring Budget 2023, the RPI annual inflation rate for 2023 was forecast to be ten percent, and 5.1 percent for 2024. With inflation proving more persistent than previously expected, this may be revised even further upwards in the future. From the same budget, the forecasted inflation rate for the Consumer Price Index (CPI) was 7.5 percent for 2023, and 3.6 percent in 2024.
Inflation eating into UK living standards
For UK consumers, high inflation is one of the main drivers of the current Cost of Living Crisis. With wages struggling to keep up with the pace of inflation for a long period between 2021 and 2023, UK households have seen their living standards fall significantly. In 2022/23, real household disposable income in the UK is estimated to have fallen by 2.2 percent, which would be the biggest fall in living standards since 1956. While there have been some signals that this crisis will ease somewhat in 2024, such as falling energy inflation, other factors, such as persistently high food inflation, indicate a more prolonged crisis.