Japan
The state of MVNOs in Japan
For a long time, the big three mobile network operators (MNO) in Japan dominated the domestic telecom networks: NTT Docomo, Softbank and au KDDI, who are currently listed as the most valuable domestic Japanese companies. The oligopolistic market structure has allowed them to charge high prices for cellular services, bringing them outstanding profit margins. However, downward rigidity in prices, as well as a nearly saturated market showing low growth rates have also time and again been subject to government scrutiny. Since the turn of the century, the Japanese authorities have thus modified competition policies and promoted a MVNO system in order to stimulate the market.
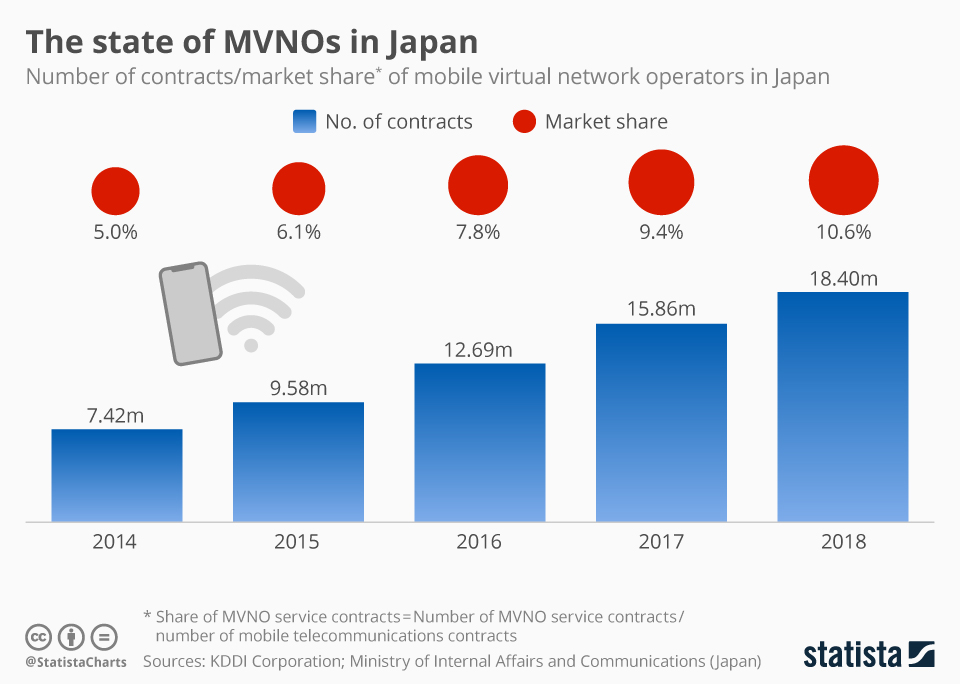
By borrowing established networks owned by the major phone companies, mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs) gain access to the networks while being able to set their own rates and plans. In the absence of infrastructure costs and in most cases brick-and-mortar stores, MVNOs can offer cheaper cellphone plans. According to the latest annual report by KDDI, government efforts have come to bear fruit, represented in the close to 19 million MVNO contracts as of March 2018, up from around 7 million in 2014. Similarly, the total MVNO market share has more than doubled in the past four years, reaching 10.6 percent, showing that low-priced SIM services provided by UQ Mobile, Iijmio, Biglobe and many more have grown in popularity.
Description
This chart shows the number of contracts/market shre of mobile virtual network operators in Japan.
Related Infographics
Any more questions?
Get in touch with us quickly and easily.
We are happy to help!
Statista Content & Design
Need infographics, animated videos, presentations, data research or social media charts?
