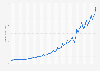
Alphabet, the company behind the video platform YouTube and the ubiquitous search engine Google, generated $238 billion in revenue from its advertising segment in 2023, which translates to online ads being responsible for 77 percent of Alphabet's overall revenue this past year. The tech mainstay's position in the advertising market is one of the key pillars of an antitrust lawsuit filed by the U.S. Department of Justice in September 2023. Hearings for the lawsuit began on September 9, 2024, only one month after Google was found guilty of breaking anti-competition laws and becoming a search monopolist. This position is also reflected in the revenues of Google's competitors in the search segment.
Company statements by Microsoft, Baidu and Yandex, a search portal formerly based in Russia and now headquartered in the Netherlands, show that even with users' preference for one or the other search engine in specific markets, advertising revenues are only a fraction of those of Google. For example, Yandex holds a 64 percent search engine market share in Russia, but only managed to generate revenues of $3.7 billion in 2023. Baidu, thought to be the leading search engine in China, with Statcounter putting it at around 53 percent market share in August 2024, recorded annual revenues of $10.6 billion in 2023, an increase of eight percent in Chinese yuan countered by unfavorable exchange rates.
Even when disaggregating Google's advertising revenue by subsegments and factoring in Microsoft doubling its search and news advertising revenue from 2021 to 2022, the playing field is still far from level. The Google Search segment alone netted the company $175 billion in 2023, according to its most recent annual report. Given these circumstances and the precedent set by the first antitrust lawsuit lobbed at the U.S. tech company, the second antitrust case against Google could very well result in another loss.